Insights
- category:
Telecoms in Africa – the challenges and opportunities

Digital technologies have brought a few new opportunities. The usage of smart devices has stimulated customer demand for new services that offer a more personalized experience. The competition has increased. There’s also pressure on pricing and regulation of the sector. To remain relevant, the telecom industry must look for new ways to differentiate itself. Investing in digital technologies is critical to increasing growth and access to connectivity. The same goes for telecom in Africa.
Key challenges in the African digital market
The traditional market continues to decline in relevance, the same as traditional telco offerings are losing to new digital technologies. The African digital market is no different. Operators are beginning to think about switching to new services. They will need to make significant changes in the infrastructure and evolve their business models to compete in the market. But they also need to confront a few challenges.

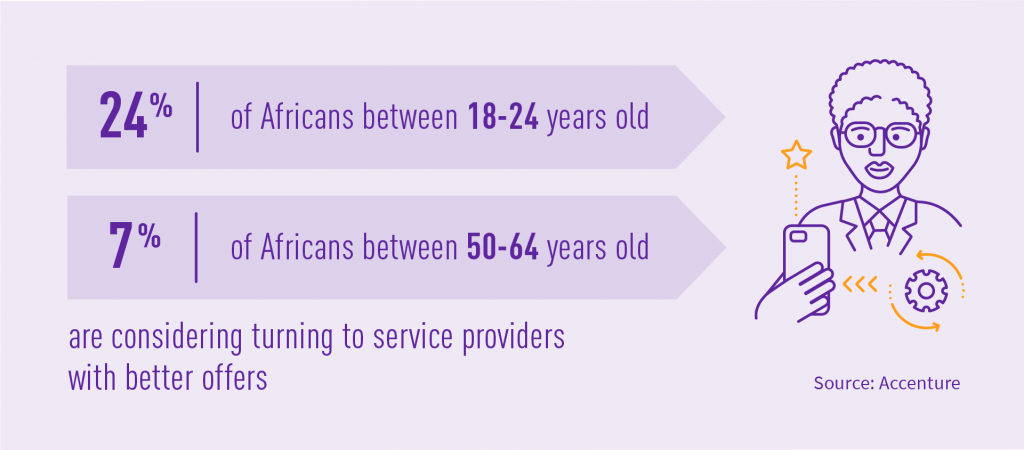
The high cost of mobile devices and Internet connectivity is one of Africa’s key challenges. Internet dispersion in South Africa is at 54%, and connectivity costs are among the highest in emerging markets. Such issues narrow the potential market for digital services and slow adoption to the new reality. The situation will be heightened by a widening gap in digital literacy between the population with access to the Internet and the one with lower access.
Companies in Africa should continue CAPEX investments in infrastructure from traditional private telecom operators, new companies, and the public sector to address these issues. But there is also a bigger question – how and where stakeholders in the telecoms sector can most effectively apply digital technologies investments to drive value for business, industry and society. They need to think about investment that will stimulate economic growth, open up more opportunities, and improve Africans’ lives.
Developing a telecom in Africa
Telecoms need to implement a dual strategy to become a leading player and respond quickly to the industry’s challenges. This requires protecting the traditional revenue streams such as voice and traditional data services while also determining the pace for turning into offering new services to offset revenue losses.
By adopting such a strategy, the telecommunications sector can continue increasing its contribution to the South African economy and protecting and growing its own market share. Four digital themes will address the main challenges within Africa’s telecommunications sector, being the basis for delivering modern and relevant solutions and competing in a new digital market.
Redefine customer engagement
Customer expectations are changing faster than ever. People are always connected to the Internet. They also have high expectations for services. High quality, seamless and personalized experiences – customers need that. Telecom operators gather substantial data about their customers, and they can use it to redefine customer engagement. New digital tools and data analytics allows gaining a deeper insight into customer behaviour, needs and preferences. If used right, it can guarantee a more personalized service experience. Telecom operators can benefit from greater customer lifetime value, reduced churn and lower acquisition and service costs.
Focus on better communication
How people communicate continues to evolve. Digital transformation and its increasing importance present the telecoms industry with opportunities to extend revenue streams. Digital services, IoT, and re-imagining communications with VR/AR are the future that could unlock a total of R76 billion by 2026. New opportunities are providing new video, advertising, insurance and payment offerings. Also, IoT services such as wearables, the connected home and connected car are gaining market power. For their enterprise customers, telecom players can leverage digital services and IoT to offer solutions from areas such as security, unified communications, cloud services, asset management and smart metering.

Implement networks of the future
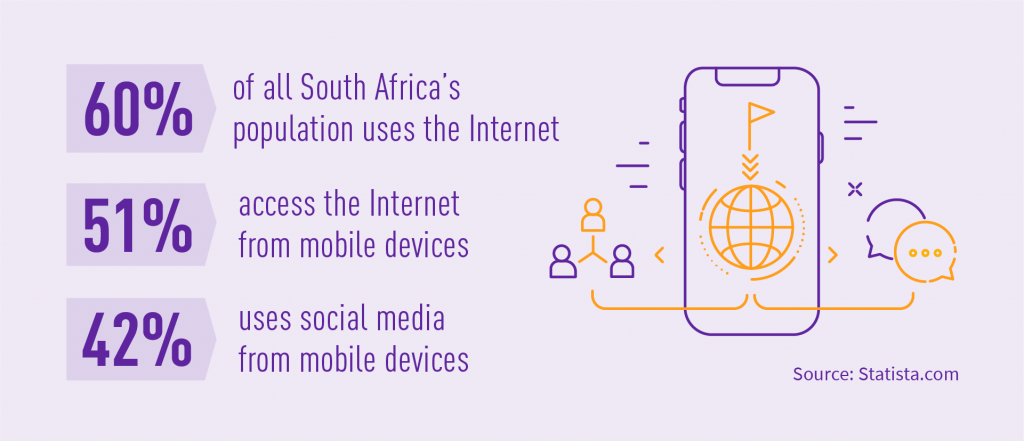
Internet accessibility is a basic commodity around the world. However, Internet penetration in Africa is only around 54%, and most people are using mobile devices to connect. Future networks in Africa can be shaped by alternate connectivity, software-defined networks, zero-touch networks, and cyber resilience. Traditional network access is becoming more and more uneconomical for network operators, especially in remote rural areas. That’s why the implementation of lower-cost solutions like Wi-Fi is so popular. This has provided the opportunity for new companies to develop new and innovative low-cost solutions to extend broadband connectivity with drones, satellites and hot air balloons. However, the implementations of 5G networks, SDN and NFV are emerging.
The evolution of the Internet, and 5G in particular, should focus on a network architecture that integrates different technologies (like Wi-Fi and cellular) and leverages multiple spectrum bands, taking into consideration spectrum and cost constraints (for operators and customers), and the possibility for customers to seamlessly switch to different network types.
Deliver innovations
Investing in new IT and network infrastructure is becoming prohibitively expensive for telecoms in Africa. While 5G can change Internet speed and connectivity, its implementation requires new infrastructure. Telecom operators’ investments in new technologies create an opportunity for new innovative customer solutions. A further effect is that customer demands continue to evolve, forcing telecom operators to adapt innovative models rapidly. Those companies that can successfully switch to digital innovations will increase in revenues. But to bridge the gap between tradition and innovation, they will also need to re-imagine ways of work, cooperate to share the risk, and continue investing in new opportunities under an agile work model.
A few use cases showing the importance of telecoms in Africa
Understanding the value of digital technologies can help lay the groundwork for innovative strategies, guiding efforts and investments to deliver growth across the telecom sector effectively. Over half of all website traffic in Africa comes from mobile devices. Therefore, the development of the telecom industry in Africa is a must. Here are a few use cases that prove it can be done right.
IPSoft
Telecom operators are looking for new ways to improve their customer service and provide the best possible digital experience. One solution that can help with that is a conversational AI chatbot. IPSoft implemented Amelia, an AI-powered virtual agent that uses natural language processing to personalize customer interactions. It recognizes users’ moods and emotions, enabling real-time conversation while also delivering personalized experiences at the same cost as a traditional customer care centre.
AI conversational chatbots are becoming more and more popular worldwide. If you are interested in our product, visit Actionbot’s website. Automating processes, improving customer care, or recommending personalized services – Actionbot can do it all!
Telenor
In 2013 Telenor, one of the leading Nordic telecom players, partnered with Volvo to create the Volvo On Call (VOC) service. This subscription service features an app that puts owners in constant touch with their vehicles. The app enables remote checks and control of the car and a host of other remote functions, such as integrated emergency and roadside assistance.
OneWeb
Programmes such as OneWeb, which will see 900 low orbital satellites connect the world and emit LTE, 3G and Wi-Fi, aim to provide affordable Internet access to the world population, bridging the digital divide around the world by 2027. OneWeb could disintermediate traditional telco players unless they rethink the network landscape. OneWeb is already working with governments, Internet service providers, mobile operators and other partners to provide the infrastructure globally.
Vodacom
In August 2018, Vodacom announced the launch of Africa’s first commercial 5G network in Lesotho. This service will only be offered to two enterprise-class customers initially. Vodacom’s 5G service uses a 3.5GHz wireless spectrum to provide consumers with “fibre-like” internet speed. This initiative is a big accomplishment for Africa. Still, Vodacom will only provide the service in South Africa and the rest of the continent once approvals are in place and the spectrum is made available.
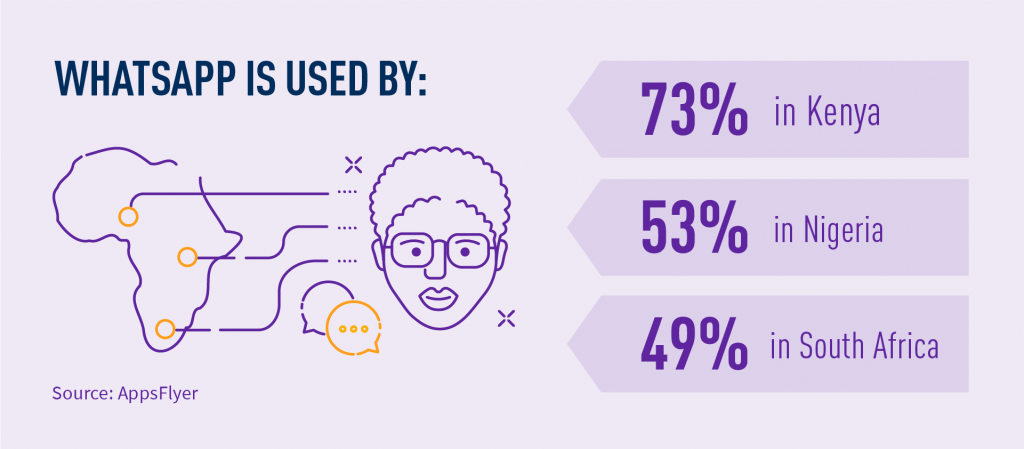
When Facebook acquired WhatsApp, it had 35 engineers and reached about 450 million users. Two years later, they exhibited a small start-up mentality and culture, employing only about 57 engineers, though the number of WhatsApp users had doubled. WhatsApp’s success in Africa is an example to learn from. It is the most popular messaging app in most African countries.
The following features made it so widely successful in this region:
- Adjusted to unstable internet service,
- Available on inexpensive feature phones,
- Unlimited data transition from photos to videos to documents to spreadsheets,
- Available for free,
- Allows sending audio messages, which is important in countries with high illiteracy rates,
- Simple to use.
TASIL supports telecoms in Africa
The telecom industry is continuously expanding across Africa. With more and more solutions being discovered and utilized by mobile operators, media owners, and third-party ad networks, this medium’s scope and demand continuously explode. TASIL is always open to showing its possibilities in other countries, and with its easy-to-implement approach, it can be a perfect opportunity.