Insights
- category:
Big Data – what’s all this fuss about?

The concept of Big Data has been more and more noticeably present in the everyday dictionary of each digital company during the last few years. Everyone feels that Big Data is not only a good direction but, frequently called the oil of the 21st century, may even become a gold mine. What exactly is Big Data, what value and what potential does it have and, last but not least, how to take advantage of it?
In the beginning, it is worth mentioning that data in its raw form has no significant value. Only processed properly gains its importance.
Big Data refers to a large volume of diverse and fluctuating sets of structured and unstructured data that requires a different than traditional handling techniques and processing approach in order to uncover the insights, data meaning and eventually to get valuable business insights.
Processed data is information. Processed information is knowledge. Processed knowledge is wisdom.
Ankala V. Subbarao
In 2001 META Group published a report presenting Doug Laney’s 3V model according to which Big Data can be described by three values:
- Volume (quantity: organizations collect data from a variety of sources: business transactions, social media, data from sensors, data exchanged between devices),
- Velocity (speed: data is created and delivered extremely fast and must be handled with an appropriate near real-time regime),
- Variety (diversity: data comes in a variety of formats ‑ from structured, numerical data in traditional databases to unstructured text documents, email, video, audio, data storage tags or financial transactions).
It helps to find the answer to trends and customer behaviours before a particular question has even been asked. Now, bearing in mind that collecting, processing and analysing large amounts of data allows obtaining new knowledge, how to make the best use of it and improve a process of business decision making?
Big Data in practice
Big Data is applicable everywhere where a large amount of data is accompanied by the need to acquire new information or knowledge. A set of demographics, behavioural and location data allows analysts to understand the motivations of customers and their choices and finally optimize activities to be taken.
Thanks to this, they know, for example, how to recognize customers’ interests and preferences or differentiate dissatisfied customers from those who are contented. The results of data processing and analysis enable identifying, for instance, which communication channels are more effective than others and therefore allow generating higher profits. It affects the organization’s development in virtually every market sector.
Banking sector
Big Data allows for gaining comprehensive knowledge which is the key to understanding the client and increasing his satisfaction by offering him the best-tailored services. It is also a perfect tool to minimize risk and reduce potential fraud as well as ensure compliance with the regulations of supervisory institutions.
Telecommunication sector
In the telecommunication sector analysing Big Data is used for monitoring network traffic which enables forecasting network capacity, network services optimization and thus improvement of services. It facilitates customer acquisition and retention, improves the quality of customer experience and customer service as well as reduces customer churn. Based on usage patterns derived from Big Data, products and services can be customized. It also allows using real-time marketing on a scale incomparable to other industries.
Public sector
In public institutions, it can be used to improve management, optimize costs, improve the quality of citizens’ services or counteract crime.
Healthcare sector
In the case of health protection, the reaction time as well as meticulousness and accuracy play a key role. All procedures must comply with detailed regulations. Big Data allows for discovering unknown relationships and improving patient service.
Tourism sector
Big Data in tourism is used to identify travel patterns, anticipate new trends and respond to customer demands by preparing customized adequate offers, promotions, discount coupons etc. Big Data insight also allows for negotiating rates with suppliers and uncovering hidden sales opportunities. All this leads to an improvement of the client’s experience and to maximisation of the company’s revenues. It is also a sector where real-time marketing can be successfully used.
Production sector
In a nowadays very competitive market it is crucial for enterprises to analyse large sets of data in order to improve the quality of products, increase production efficiency and reduce losses.
Retail trade sector
Proper data processing and management allow for building long-lasting relationships with customers which is of great importance for development in the retail trade industry. Big Data helps traders develop optimally and the most effective ways to reach their customers and prospects, manage transactions and regain lost sales opportunities.
Big Data potential
The amount of data that is generated and stored on a global scale is not only barely imaginable, but it is also constantly growing. Still, only a small percentage of information is subject to analysis. As reported in IBM Marketing Cloud study, 90% of all information in the world has been generated in the last two years. These statistics show the pace at which the amount of data increases. In practice, this means that there is a massive potential for business-related information that has not been used yet.
Information is the oil of the 21st century, and analytics is the combustion engine.
Peter Sondergaard
Thanks to advanced analytics, data from various sources may be used for making more relevant business decisions, time and costs reduction, creating new product offers, determining causes of failure, malfunction, and defects in near real-time, detecting abusive customer behaviours before they significantly affect the organization or generating coupons, based on their shopping habits.
What does Big Data mean for marketing?
The analysis and processing of large data sets, obtained, among others, from internal systems or social media can be translated in marketing into better price management in time, better use of advertising budget, getting to know customers and their preferences, precise matching the offer to a particular customer, optimization of the path-to-purchase or reduction of the conversion costs.
Without Big Data analytics, companies are blind and deaf, wandering out onto the web like deer on a freeway.
Geoffrey Moore
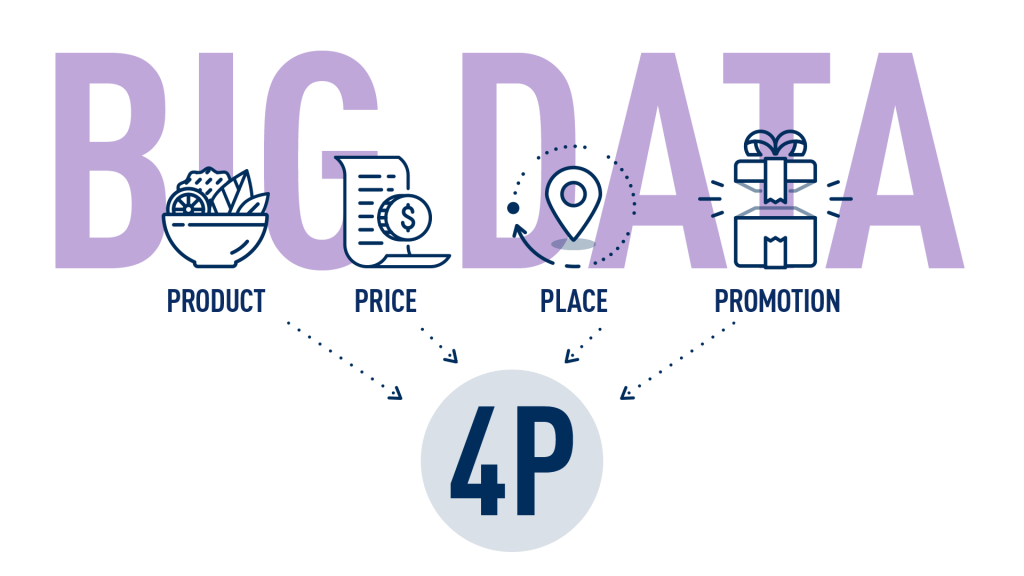
A set of elements which marketers can use to influence the market, often recognized in terms of four “P” (4P) is Product, Price, Place and Promotion. Big Data can address and improve the functioning of each of these aspects.
Product
Data on the popularity of individual products allows for identifying the most attractive products, anticipating possible demand and managing store supply. Quantitative and qualitative data also allow better developing and improving the product.
Price
Big Data allows dynamic price formation, depending on the demand. Prices can be modified at different times and increase for example in case of growing demand for products or services that run out fast.
Place
Big Data enables defining in what places the clients currently or frequently are, which thus allows choosing the most efficient communication channel and the best promotional activities.
Promotion
Appropriate data processing allows for measuring the response to the promotional tactics more accurately as well as it can help predict the reactions of specific recipients to a given product.
From the marketer’s point of view, the important data is:
- demographic data (age, gender, place of residence, nationality)
- behavioural data (products added to the cart but not bought, previously viewed products, browsed subpages, time spent on individual subpages, materials viewed, reactions to individual marketing campaigns, geolocation, mentions about the brand in social media)
- transaction data (previously purchased products, average value of the shopping basket, frequency of purchases)
- the user of the mobile application data (how long the application has been used, how often, which modules are used most often, reactions to mobile marketing messages, what are the other applications installed on the device)
- declarative data (the information that users provide in surveys or questionnaires)
- operational data (the quality of marketing processes related to marketing operations in an organisation, resource allocation, asset management, budget control, etc.)
- financial (may include data on sales, revenues, profits as well as other types of data measuring the financial condition of an organisation)
It is important to remember that obtaining a complete view of a customer, organisation’s condition and converting data into specific marketing actions often requires integrating many tools, e.g. tools analysing user behaviour on the website and in the mobile application.
Big Data marketing in practice
According to the Global DMA / Winterberry Group report, marketers indicate 5 most important practical applications of Big Data in their industry:
- targeting offers, news and content (69% of respondents)
- strategy building or product development (52% of respondents)
- customer experience optimization (49% of respondents)
- traffic analytics / measuring the effectiveness of actions (44% of respondents)
- predictive analytics (44% of respondents)
Other sources suggest that among the most popular Big Data applications in sales and marketing are:
- customer analytics (48%)
- operational analytics (21%)
- fraud and compliance (12%)
- new product service innovation (10%)
- enterprise data warehouse optimization (10%)
The most valuable commodity I know of is information.
Gordon Gekko
By combining Big Data with an integrated marketing management strategy, marketing organizations can have a significant impact on the following aspects:
- customer involvement – Big Data presents an insight not only of who our clients are but also provides detailed information about their location, needs and preferred ways of contact
- customer retention and loyalty – Big Data can help discover what affects customer behaviour and loyalty and what makes them come back
- marketing optimization and its effectiveness – Big Data enables optimization of marketing expenses in respective channels, as well as, thanks to tests, measurements and analyses, it allows constant marketing strategies optimizing
The effective use of Big Data presents a challenge for marketers. The three most important challenges are:
- knowing which data is relevant
- choosing the right analytical tools
- the transition from data through knowledge to impact
To make sure that using Big Data will provide measurable marketing success, information should be delved to expose subsequent layers and discover richer knowledge resources. The knowledge gained from the original data analysis may be a subject of further investigations, allowing a fuller, deeper understanding of the examined issues. This level of knowledge allows the creation of specific strategies and growth-enhancing activities.
Make the most of Big Data marketing with TASIL
TASIL relies on the power of real-time marketing and Big Data itself. It knows well that data is the fundament, context is the key and that cutting-edge technology is crucial to tie it all together in order to uplift your customers. TASIL helps marketers prepare the most relevant and effective advertising campaigns. It analyses the Big Data and makes the best possible use of it, so that you do not have to worry about doing it yourself and just enjoy taking advantage of the benefits of proper utilization of large data.

Based on Big Data coming from the most reliable sources, such as mobile phone operators, and processed properly, TASIL’s functionalities were created. TASIL’s filters allow easy and the most accurate campaign targeting and thus, using them increases the chances for the campaign to be successful.
Marketers can choose from 6 available filters including nationality, location, list, purchasing power, age and gender or ask TASIL to create new, custom filters.
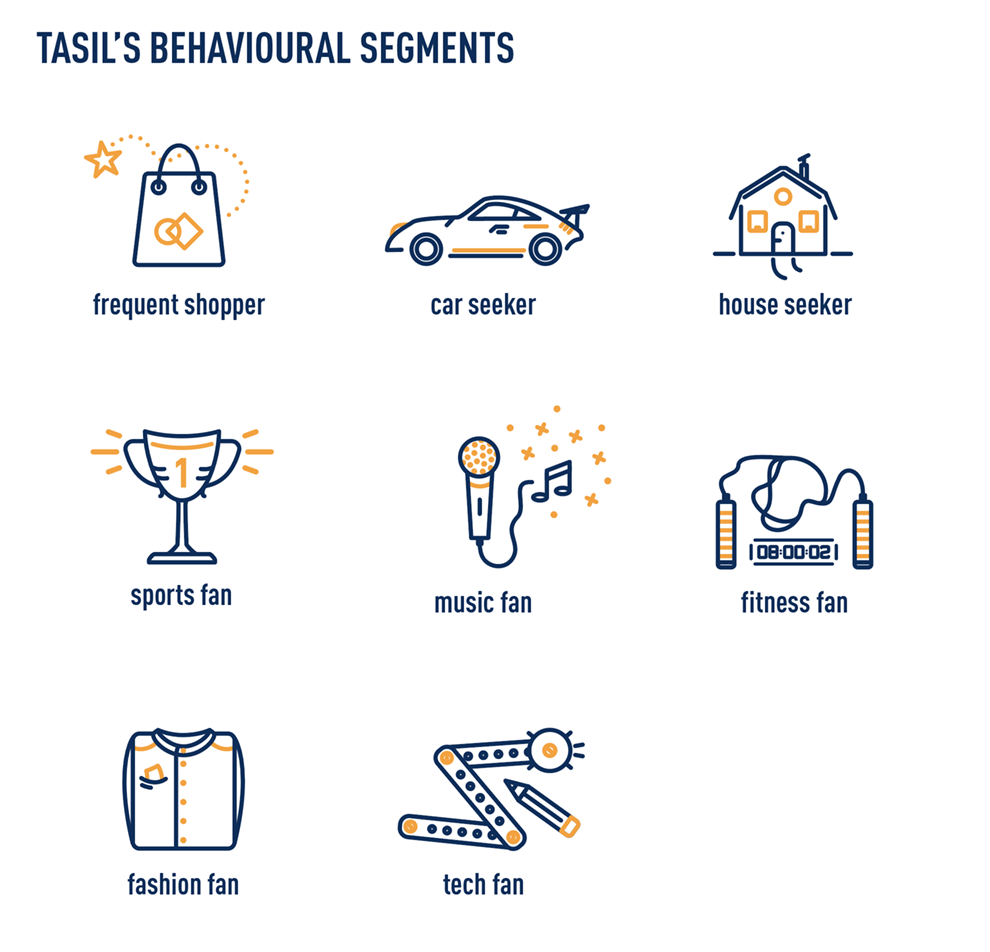
TASIL created also segments based on customers’ behaviour, based on Big Data processing and analysis as well, and these are frequent shoppers, car seekers, house seekers, sports fans, music fans, fitness fans, fashion fans and tech fans. Segments can be used jointly or separately from filters and they allow even more precise campaign targeting. It is Big Data and its analysis that allows TASIL to be always right!
Since TASIL gives the opportunity to analyse performance of each campaign thoroughly, the data deriving from such analysis can be used by the marketer for re-targeting the next campaigns, even more accurately.
Marketing activities based on Big Data are launched on an ongoing basis, in real-time, which is why they are always based on the most current information about the customer. Such a dynamic adjustment of communication and content to the real state allows reaching customers with the offer of exactly what they currently need.



